Embracing the Future: Integrating Latest Digital Technology in Endodontic Education
By Gordon Lai, DDS, MSD
As we navigate the ever evolving landscape of dental education, it’s exciting to explore how the latest advances in digital technologies can enhance our current teaching methods and improve student learning. Today, I want to share some innovative ways that we have incorporated these digital technologies at University of the Pacific, Arthur A. Dugoni School of Dentistry for the benefit of our predoctoral students as well as endodontic residents.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Endodontics
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process that creates three-dimensional objects by adding material layer by layer, based on a digital model. In endodontics, this technology has transformed the way educators and students approach complex dental procedures.
Advantages of 3D Printing in Education
- Customized Learning Aids: Traditional dental models used in education are often generic and do not cater to the unique anatomical variations found in real patients. 3D printing allows the creation of customized models that replicate specific clinical scenarios, enabling students to practice on realistic and patient-specific cases.
- Enhanced Understanding of Anatomy: Endodontic procedures require a deep understanding of the intricate structures within the tooth. 3D-printed models provide a tangible, hands-on tool for studying these structures, offering a more comprehensive understanding than two-dimensional images or diagrams.
- Simulation of Clinical Procedures: With 3D printing, it is possible to simulate various clinical procedures, from root canal treatments to complex surgeries. These simulations allow students to practice repeatedly without the risk of causing harm to real patients, thus building their confidence and competence.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: Traditional methods of creating realistic dental models and surgical guides can be expensive and time-consuming. 3D printing offers a cost-effective and rapid alternative, making it easier for educational institutions to provide high-quality training resources in house rather than relying on outside companies and laboratories.
Practical Applications in Endodontic Training
One practical application of 3D printing in endodontic education is the creation of transparent tooth models. These models allow students to observe the internal structures and the progress of their procedures in real-time. Additionally, educators can use 3D printing to develop surgical guides that assist in precise drilling and placement during endodontic surgeries, ensuring that students learn to execute procedures with high accuracy.
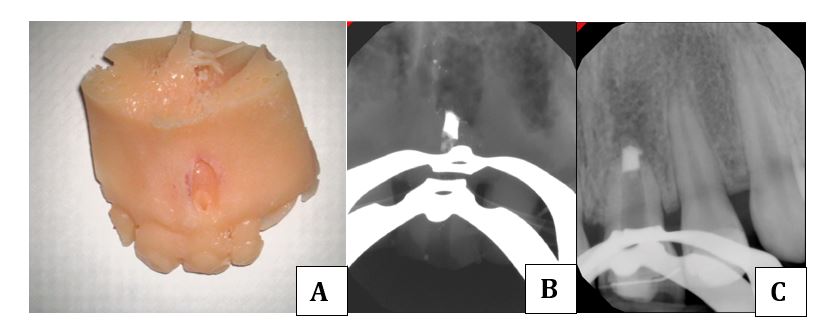 This 3D printed model (Figure A) was created specifically to help an endodontic resident on her first bioceramic putty apexification case. The model was generated based off the actual patient CBCT data so that she could practice the procedure beforehand to familiarize herself with the procedure. Figure B shows the resident’s attempt on the 3D model and Figure C shows the actual final results on the patient.
This 3D printed model (Figure A) was created specifically to help an endodontic resident on her first bioceramic putty apexification case. The model was generated based off the actual patient CBCT data so that she could practice the procedure beforehand to familiarize herself with the procedure. Figure B shows the resident’s attempt on the 3D model and Figure C shows the actual final results on the patient.
Mixed Reality in Endodontics
Mixed reality (MR) combines elements of both augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), blending the physical and digital worlds to create immersive experiences. MR has the potential to transform endodontic education by providing interactive and engaging learning environments.
Benefits of Mixed Reality
- Immersive Learning Experiences: MR enables students to interact with digital models and simulations in a way that traditional methods cannot match. For example, students can visualize the anatomy of a tooth in 3D, rotate it, and observe it from different angles, gaining a deeper understanding of spatial relationships and complex structures.
- Real-Time Guidance and Feedback: During clinical procedures, MR can provide real-time guidance and feedback. By overlaying digital markers and instructions onto the physical anatomy of a patient, students can receive step-by-step assistance, reducing the likelihood of errors and improving the quality of their work.
- Increased Engagement and Retention: The interactive nature of MR makes learning more engaging and enjoyable. Students are more likely to retain information and develop a genuine interest in the subject when they are actively involved in the learning process.
- Remote Learning Capabilities: MR technology can create virtual classrooms and training sessions, allowing students from different geographical locations to participate in high-quality education without the need for physical presence. This is particularly beneficial in the current global scenario, where remote learning has become increasingly important.
Implementing Mixed Reality
One of the most promising applications of MR in endodontics is the development of MR-based training modules. These modules can guide students through various procedures, such as root canal treatments, by overlaying digital instructions onto a physical model or even a real patient. Additionally, MR can be used to create virtual patient simulations, where students can practice diagnosing and treating dental conditions in a controlled, risk-free environment.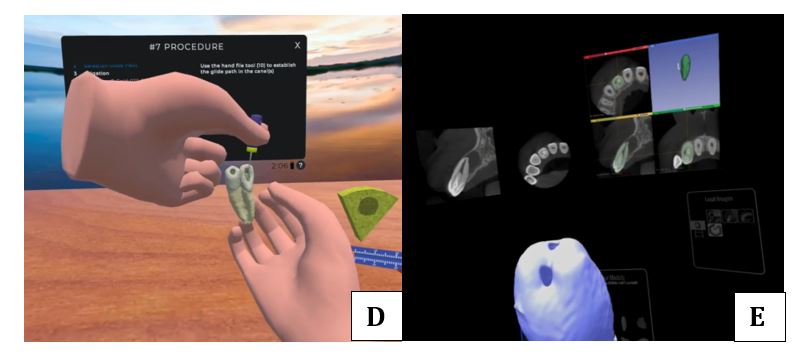 Figure D shows an example of creating an unique gemination tooth model based off patient’s CBCT data to allow residents to practice working on this rare anatomy. Figure E shows a case being treatment planned in the VR environment which allows the operator to study the relevant CBCT data, along with radiographs and the 3D model of the tooth that can be freely rotated and magnified as needed.
Figure D shows an example of creating an unique gemination tooth model based off patient’s CBCT data to allow residents to practice working on this rare anatomy. Figure E shows a case being treatment planned in the VR environment which allows the operator to study the relevant CBCT data, along with radiographs and the 3D model of the tooth that can be freely rotated and magnified as needed.
Embracing the Future
As technology continues to evolve, the possibilities for integrating 3D printing and mixed reality into endodontic education are limitless. Future advancements could include the use of AI to personalize learning experiences, the development of more sophisticated VR/AR simulations, and the incorporation of haptic feedback to better simulate the tactile sensations of dental procedures.
Incorporating these technologies along with other advances in digital technology into our endodontic education programs holds immense potential to revolutionize how we teach and how students learn. By embracing these innovations, we can provide more engaging, effective, and personalized education experiences that prepare our students for the challenges of modern endodontics.
Let’s continue to explore and experiment with these technologies, sharing our successes and learning from each other.
Gordon Lai, DDS, MSD, is an assistant professor at the University of the Pacific, Arthur A. Dugoni School of Dentistry in San Francisco.
